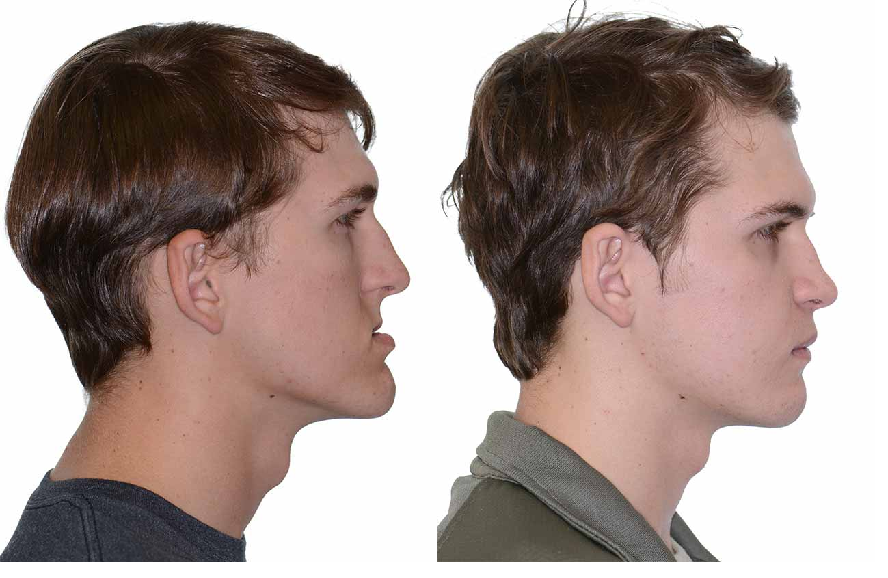
Advancement of the jaw, square jaw, lower jaw too short, open bite… Not only are these malformations causing aesthetic and psychological suffering, but they can also be the cause of functional disorders (swallowing, breathing or chewing).
Orthognathic surgery concerns interventions aimed at correcting malformations or accidental deformations of the jaws. His goal ? Improve the positioning of teeth and jaws. Are you considering orthognathic surgery? Price, procedure, principles… Here is everything you need to know.
Orthognatics: practical information
The majority of patients consult a surgeon for a maxillofacial procedure following orthodontic treatment. Indeed, orthognathic surgery will make it possible to resolve malformations, moderate to severe, which cannot be treated by orthodontics. That being said, following the operation, it is strongly advised to continue orthodontic treatment for optimal and lasting results.
This type of intervention is possible once growth is complete, approximately from the age of 16.
Jaw surgery: objectives and principles
During this surgical act, the practitioner intervenes on the facial skeleton (in particular the bones of the maxilla and/or the mandible) to restore a good position to the jaws and/or teeth.
There are different scenarios:
Severe malocclusions : These are dental malpositions. The lack of space in the jaw creates rotations or overlapping of the teeth. It happens that the upper teeth are too forward or that they cover the lower ones.
Severe prognathism : When the lower jaw is longer than the upper jaw.
Severe retrognathia : This malformation designates a too short lower jaw which is responsible for functional disorders, pain and abnormal wear of the molars. Orthognathic intervention, usually accompanied by genioplasty , is to be expected.
First, the surgeon performs an assessment. He will study the disorders, the state of the teeth and the shape of the face. During this exchange, the patient explains to the practitioner his wishes and motivations, whether functional or aesthetic. To complete this assessment, photos, x-rays and casts are made. The practitioner can then explain the type of intervention envisaged and the different stages to be planned. A tailor-made quote is established at this time.
In consultation with the orthodontist, the surgeon can request orthodontic treatment before the orthognathic operation. He may also recommend consulting a pulmonologist (in case of sleep apnea, for example) or a physiotherapist.
A preoperative assessment makes it possible to plan the course of the operation down to the smallest detail and to calculate the new position of the jaws. The surgeon can have surgical guides made to be used during the surgery.
Essential, the anesthesia consultation must take place at least fifteen days before the operation, in order to be able to plan additional examinations if necessary.
before the intervention, have consulted his dentist to have treatment and scaling carried out.?
Orthognathic surgery: type of anesthesia and hospitalization procedures
Orthognathic surgery is performed under general anesthesia, either on an outpatient basis (the patient can go home the same evening) or during a short hospital stay (one or two days).
On the day of the operation, it is necessary to arrive on an empty stomach, after taking a full shower and carefully cleaning the teeth and nose.
Jaw surgery: the procedure
The operation lasts between 1 and 4 hours. The maxillofacial surgeon makes incisions inside the mouth and then cuts in the jaws. He will then position them as decided during the preoperative consultation. Finally, using screws and plates, he secures the positions of the bones. The incisions are then sutured with absorbable sutures. After a few hours in the postoperative room, the patient can return to his room. It is important to note that he is able to drink and talk, as the jaws are not locked, as they might have been many years ago.