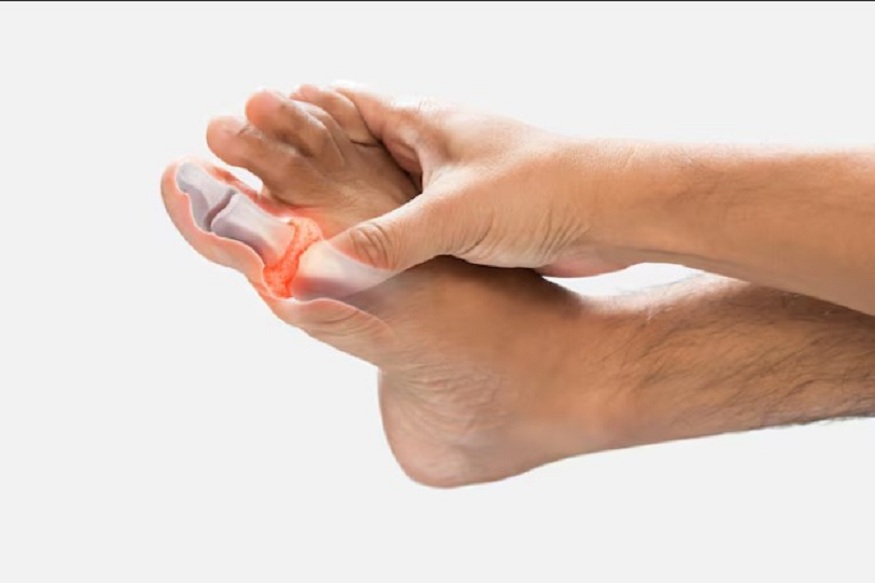
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis that can cause sudden, intense pain, swelling, and redness in the joints, most commonly affecting the foot, especially the big toe. These episodes, known as gout flare, can disrupt daily life and significantly impact mobility.
Understanding what triggers these flares, recognizing the symptoms early, and knowing how to manage them effectively is essential for anyone dealing with gout. In this blog, let’s discuss how to manage the flares of gout.
What Is Gout?
Gout occurs when there is a buildup of uric acid levels in the blood. Uric acid is a natural waste product that forms when the body breaks down purines, substances found in some drinks and foods. Uric acid is often dissolved in the blood and excreted via urine. However, if the body produces too much uric acid or fails to eliminate enough, crystals can accumulate in the joints, causing inflammation and excruciating pain.
While gout can affect anyone, it is more common in men over 40 and postmenopausal women. Lifestyle factors, genetics, and certain medical conditions can also increase the risk.
What Are The Symptoms Of Gout?
Recognizing gout symptoms early can help manage flares more effectively. Key signs include:
- Severe Joint Pain: Usually starts suddenly, often at night. The big toe is commonly affected, but ankles, knees, wrists, and elbows can also experience gout pain in the foot.
- Swelling And Redness: The affected joint may appear swollen, tender, and warm to the touch.
- Limited Mobility: Pain and swelling can restrict movement in the affected joint.
- Lingering Discomfort: Even after the flare subsides, joint discomfort can persist for days to weeks.
Severe gout attacks can be debilitating, making early intervention crucial.
What Are The Common Causes Of Gout?
Several factors contribute to the development of gout, often related to high uric acid levels. Common causes include:
- Dietary Choices :Consuming foods high in purines, such as red meat, seafood, and organ meats, can raise uric acid levels. Alcohol, particularly sugary drinks, and beer can also contribute.
- Medical Conditions: High blood pressure, diabetes, kidney disease, and metabolic syndrome increase the risk.
- Medications: Certain diuretics, aspirin, and medications for organ transplants can elevate uric acid.
- Genetic Factors: A family history of gout may predispose individuals to developing the condition.
- Lifestyle Factors: Obesity and lack of physical activity can exacerbate uric acid accumulation.
Understanding these causes helps in preventing and managing future flares.
How Can Gout Be Managed?
Managing gout effectively requires a combination of medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and self-care strategies.
1. Medical Management
Consulting the best rheumatologist doctor in Coimbatore can provide personalized treatment plans. Common approaches include:
- Medications To Relieve Pain: These are often prescribed during acute flares.
- Medications To Reduce Uric Acid: Long term management may include drugs that lower uric acid production or improve its excretion.
- Regular Monitoring: Periodic checks of uric acid levels help in adjusting medications and preventing future flares.
In case you have severe gout pain, getting specialized treatment from the best rheumatologist in Coimbatore can offer you with advanced diagnostics, and comprehensive follow up care.
2. Lifestyle And Home Remedies
Several practical measures can help reduce the intensity of flares and prevent recurrence:
- Dietary Modifications: Limit purine rich foods like red meat, seafood, and sugary beverages. Increase intake of low fat dairy, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Hydration: Consume a lot of water to help flush uric acid from your body.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy body weight decreases the stress on the joints and reduces uric acid levels.
- Limit Alcohol: Particularly alcoholic beverages can provoke flares.
- Cold Therapy: Applying ice packs to the affected joint can relieve swelling and pain during flares.
- Rest And Elevation: Keep the affected foot elevated to reduce discomfort and swelling.
3. Preventive Measures
- Regular Exercise: Low impact activities like swimming or cycling help maintain joint flexibility.
- Routine Checkups: Regular visits to a rheumatologist help monitor uric acid levels and overall joint health.
- Medication Adherence: Following prescribed medications consistently prevents recurrent flares.
By combining medical treatment with lifestyle adjustments, most people can manage gout effectively and enjoy a better quality of life.
Key Takeaways
Gout is a manageable condition if addressed promptly and appropriately. It results from high uric acid levels and often affects the foot, causing intense pain. Early recognition of symptoms like swelling, redness, and limited mobility is crucial, as is understanding common triggers, which include diet, medical conditions, genetics, and lifestyle factors.
If you have severe pain, limited mobility, swelling, and redness in the affected joint, then getting proper diagnosis at the best rheumatology hospital in Coimbatore ensures expert guidance and optimal outcomes.
By knowing how to reduce gout pain during flares and taking proactive steps, individuals can significantly improve mobility, reduce discomfort, and prevent long term joint damage, allowing them to continue leading an active, healthy life.